Ruchi Gakhar
University of Wisconsin Madison, USA
Title: Characterization of graphite components of FHR design
Biography
Biography: Ruchi Gakhar
Abstract
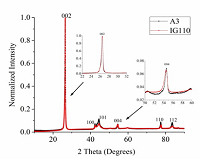
Two types of graphite used in the core design of Fluoride Salt Cooled High Temperature Reactor (FHR) are Graphite Matrix A3 and Nuclear Grade IG110. Matrix A3 forms the structural component for the fuel kernels, while IG110 forms the reflector blocks and some of the internal core components. Graphite forms an integral component of this design because it contributes to the structural integrity of the reactor as well as the pores of the graphite are considered as the main trapping site for the tritium produced in the coolant salt. Matrix A3 graphite which forms fuel pebble contains fission product that are produced during nuclear operation. In addition, the salt coolant or the corrosion products might intrude through the surface into the pores of the graphite. Considering these attributes, the microstructure characterization of two grades of graphite is important in developing knowledge of characteristics of graphite under FHR operating conditions. The microstructural differences between A-3 and IG-110 are attributed to the differences in the raw materials and the heat treatment temperature during manufacturing . The present study focuses on the microstructure examinationof two types of graphite components using X- ray Diffraction, Raman Spectroscopy, BET analysis, Mercury porosimetry and Scanning Electron Microscopy techniques. The lattice parameters crystallite size (parallel and perpendicular to the basal plane), anisotropy and degree of graphitization estimated based on X-ray diffraction patterns and Raman spectra for both IG-110 and Matrix A3 graphite, will be discussed. The similarities and differences in microstructural characteristics between the two grades of graphite as obtained using the XRD and Raman spectroscopy results will be presented and the factors causing such differences will be discussed.