
Dandan Xu
Beijing Forestry University, China
Title: Ionic liquid-stabilized graphene and its use in decorated with Co nanocatalyst towards chlorinated organic pollutants degradation
Biography
Biography: Dandan Xu
Abstract
Tremendous efforts have been devoted to find methods with high-efficient and low-cost to remove chlorinated organic pollutant from aqueous solutions. Metal nanoparticles modified graphene materials have attracted considerable attention, but the limitation is the difficulty in depositing metal nanoparticles with uniform size and good dispersion on graphene surface. Ionic liquid (IL) shows potential for overcoming some of the above mentioned issues due to their high chemical and thermal stability, negligible vapor pressure, high conductivity and wide electrochemical window. This paper involved functionalization of graphene samples with IL ([Bmin][BF4]) and in situ reduction of cobalt precursors to improved their electrocatalytic performance and application on electrochemical degradation of chlorinated organic pollutants. Several characterization methods such as XRD, SEM and XPS were used to analyze prepared samples crystal structures, surface morphology, composition and nanoparticles size. XPS measurement showed the wide survey XPS pattern of catalyst, which indicated the coexistence of C, N, O and Co in the catalyst, and element N was originated from the IL. The sizes of Co nanoparticles on Co/IL-graphene (3.33 nm) was smaller than that on Co/graphene (6.60 nm) due to stabilization of IL. Electrocatalytic measurements revealed Co/IL-graphene catalysts displayed enhanced current response compared with Co/graphene samples. And a strong reduction peak at 0.036 V presented for Co/IL-graphene which was quite different from the Co/graphene catalyst. It indicated that the Co nanoparticles IL functionalized graphene had a significant electrocatalytic activity. The addition of IL can not only improve the dispersity of Co nanoparticle, but also increase the active sites. The Co/IL-graphene nanocomposite will be suitable materials for degradation of chlorinated organic pollutants in aqueous solutions.
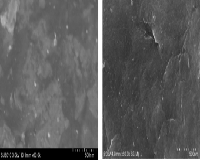
Figure 1: SEM patterns of the Co/graphene (a) and Co/IL-graphene (b) catalysts.
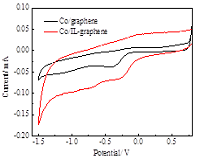
Figure 2: CV curves of different catalysts in an alkaline solution (pH=12.8).

